|
- |
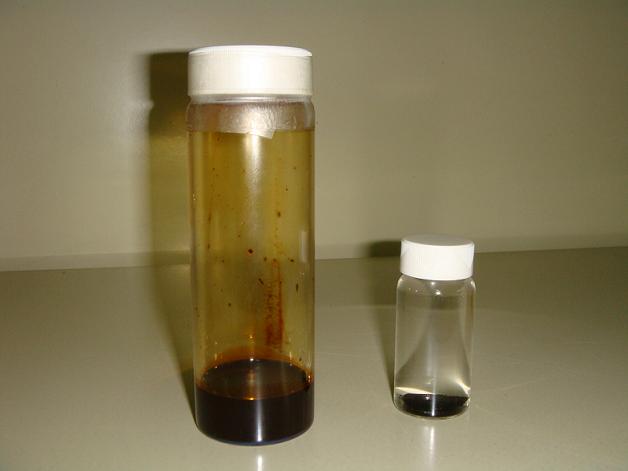
研究成果: 奈米科技(nanotechnology)係指至少有一特徵尺寸處在奈米尺度(nanoscale)所涉及的科學及技術,該尺度特別是指尺寸小於100 nm。奈米結構(nanostructures)係指由大小在1 nm至100 nm範圍內的原子或分子所組成的材料和系統結構(material and systematic structures)。典型的奈米結構包含奈米粒子(nanoparticles)、奈米孔(nanopores)、奈米絲(nanofilaments)、奈米線(nanowires)、奈米棒(nanorods)、奈米管(nanotubes)、奈米膜(nanofilms)及奈米層(nanolayers)等,由於係由有限的粒子或分子所構成,可以設計為具有新穎且顯著改善的機械、熱學、化學、磁學、光學、電學及生物學特性。流體內懸浮奈米粒子稱為奈米流體(nanofluids),若流體內的奈米粒子具有磁性,此類流體稱為磁性奈米流體(magnetic nanofluids),或簡稱為磁流體(magnetic fluids),亦稱為鐵磁流體(ferrofluids)。針對鐵磁流體流體動力學(ferrohydrodynamics)問題,我們先前曾完成外部磁場梯度(external magnetic field gradient)對磁性奈米流體懸滴輪廓(pendant droplet profile)之影響,並提出另一磁化場方程式(magnetization equation)- WCC模式,WCC模式相較於過去文獻所提之Sh72、Feld、Sh01、ML及WC等模式可更合理解釋磁化場強度(magnetization)及磁黏滯係數(magnetoviscosity)的實驗結果。此外,我們開始研究粒子內磁矩(magnetic moments)自旋對非牛頓流動(non-Newtonian flow)的影響,並回顧了具有微/奈米結構(micro/nanostructure)的流體其流體動力學中不同場方程(field equations)的論點,並闡明其本質的定性(deterministic nature)。近期,我們於2015年探討微管道(microtube)內磁性奈米流體對流熱傳(convective heat transfer)之問題,並實驗探討微管道內粒子與粒子及粒子與牆表面間的碰撞及摩擦效應。於2016年設計了一可測試磁性奈米流體潤滑液之液靜壓軸承測試系統(hydrostatic bearing test system)。於2017年探討了外部磁場梯度對磁性奈米流體座滴輪廓(sessile droplet profile)之影響。於2018年進一步提出了磁性奈米流體於不同AAO奈米孔表面受磁場作用之靜態與動態濕潤性的探討。於2020年合成了Co2+摻雜的BiOBrxCl1-x分層奈米結構微球(nanostructured microspheres),結果顯示了出色的光催化性能(photocatalytic performance)。 |
| 圖示說明 |
|
˙微奈米流體力學 |
 |
|
˙微奈米流體力學
To investigate the influence of magnetic forces on magnetic fluid pendant drop profile, a magnetic fluid pendant drop in an applied magnetic field was considered first. Then, according to the normal stress balance principle, the Young-Laplace equation was revised, and the revised nonlinear differential equation was further solved. Finally, the drop profile data of magnetic fluids were determined, so as to investigate the magnetic force effect on liquid drop behavior. |
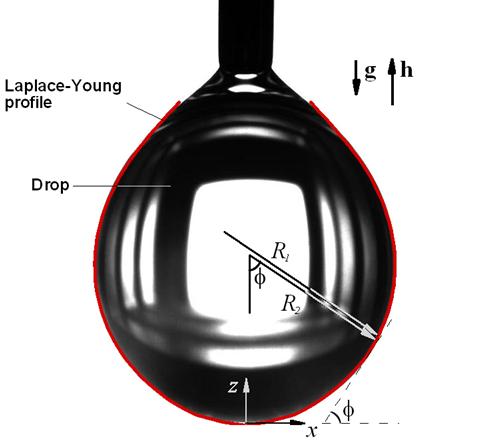 |
|
˙微奈米流體力學 |
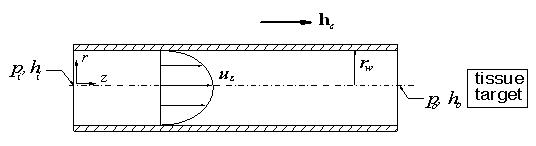 |